What’s in Your B2B Customer Experience Function?
What’s in your customer experience function? This is not a trick question. The definition of customer experience is a moving target. We know this because we asked more than 200 B2B companies with a customer experience function what they include in it.
What we found is that most organizations have room to evolve the customer experience function and realize more of its potential. Many companies have already made great strides with coordination around the buyer’s journey and can do the same with aligning the post-sale customer lifecycle. Rather than letting each function determine its contributions independently, companies should use the customer experience role to create alignment without insisting on ownership. This collaborative model embraces complexity while also providing organization, and can be used to keep the customer’s point of view (and changes to it) represented in all experience decisions.
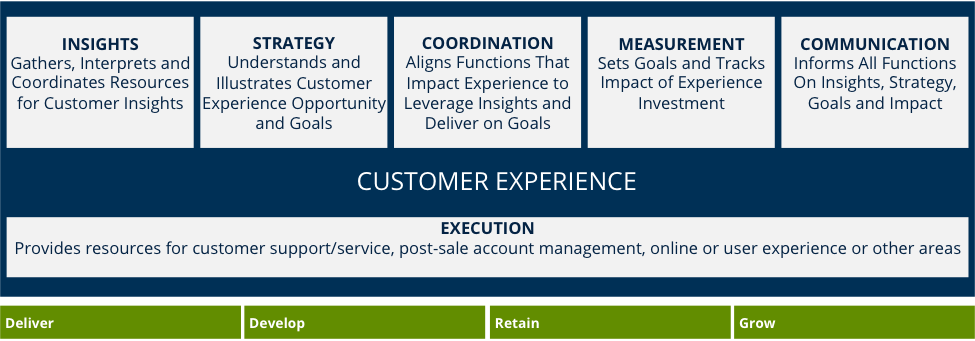
Our data shows that approximately 60 percent of B2B companies have a customer experience function in place. The most common title for the top customer experience executive is chief customer officer, but what this executive is in charge of delivering varies. Here’s a list of the areas that tend to be included in a B2B customer experience group – including the percentage of B2B companies that currently include each area in their experience teams and our observations on what each area contributes.
- Strategy (included in 81 percent of organizations). Strategy is the most critical aspect of a customer experience team’s role because it sets the tone for overall experience delivery and makes cross-functional alignment possible. Organizations that don’t have a customer experience function or don’t place it in charge of coordinating strategy often have disjointed experience delivery and missing or redundant efforts.
- Insights: voice of the customer/loyalty research (59 percent). A key mission of the experience function is to represent the customer’s perspective across the organization. This mission can be performed most effectively with a comprehensive strategy for gathering insights. The customer experience function should lead collection of relationship feedback (e.g. Net Promoter Scores or customer loyalty research). Collection of other types of feedback, from transactional surveys about online or service experience to product-focused voice-of-the-customer information to social media monitoring, can be led or supported by the experience function. When the experience function does not own insight collection, it should be aware of all the research being done and serve as a clearinghouse for the timing of outreach as well as interpreting and sharing the information across functions.
- Coordination: Customer lifecycle/journey mapping (53 percent). A mapping capability is a shared service that other functions can use for defining improvement to their experience contributions. It also provides a cross-functional perspective that shows how all areas of the business are interacting with customers. Skills include the ability to create inventory, activity and new experience maps.
- Measurement (94 percent). Measurement monitors what’s happening and tracks the impact of experience investments. Centralized measurement of experience areas impacted by cross-functional execution ensures objective evaluation of what’s happening.
- Communication (not tracked as a separate experience element in our study). The experience function uses communication to keep all others in the business informed of what’s happening, from insights to strategy to measurement. Some organizations create collaboration hubs (e.g. internal communities or online information, social collaboration tools) for sharing information and may also use email and other channels.
- Execution: Customer marketing (63 percent), customer service (59 percent), online experience (47 percent), account management/customer success team (43 percent). These functions all deliver part of the customer experience, and in some companies, the experience function includes one or more of these areas. (The percentages shown reflect the share of companies with a customer experience function who include these various areas in that experience group.) Including aspects of execution in the experience function help to ensure clarity of focus on customer engagement and the customer point of view.