Can AI Boost Product Innovation?
Not surprisingly, Forrester readers these days often ask about the impact of AI on product lifecycle management (PLM). The most typical question we get in this context refers to embedded AI versus generative AI.
Should You Embed AI In PLM Or Just Add Bard Or ChatGPT On Top?
Clients tell us that traditional AI analyzes existing data and can detect anomalies but generative AI creates new content and suggests resolutions. They agree that genAI complements to PLM are not yet ready to address safety-critical or compliance issues but can help to organize meetings, tasks, approvals, and deliverables.
Embedded AI Use Cases For PLM
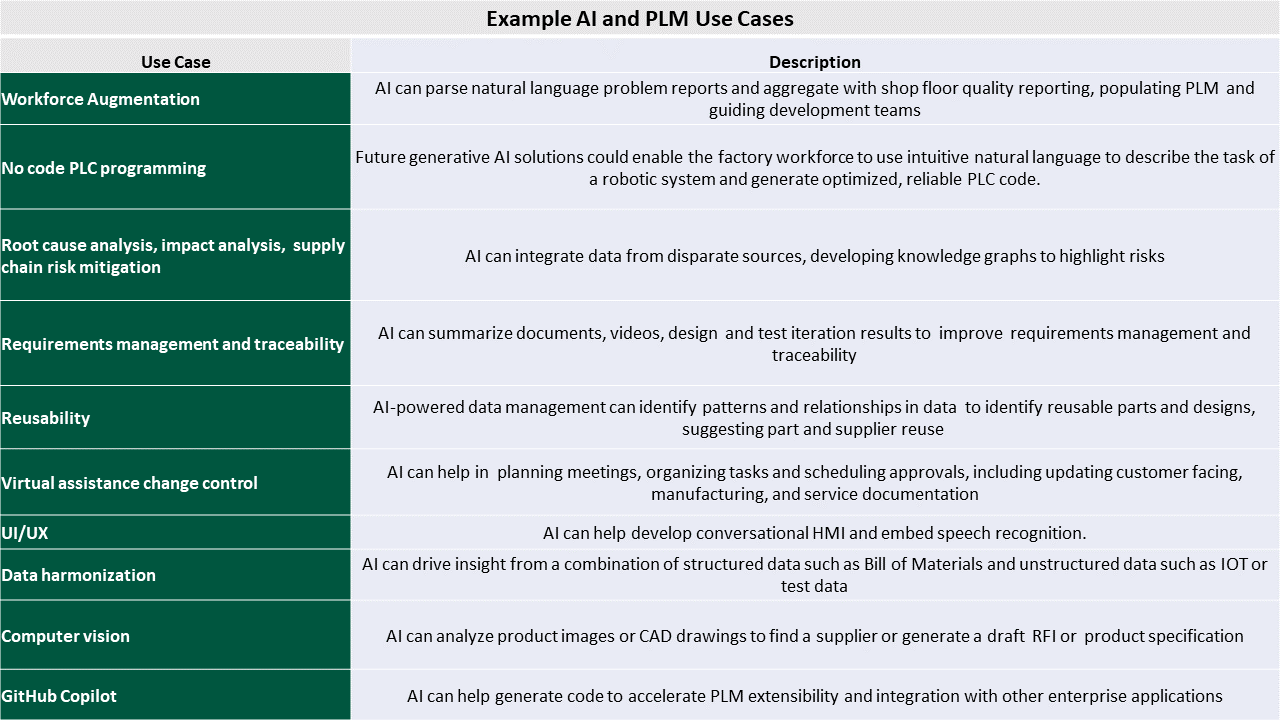
Over recent months, we have observed several examples of embedded AI in PLM platforms for use cases such as:
- Requirements management and traceability. Manufacturers expect that natural language processing and summaries of documents, videos, and other sources of data can accelerate requirements management and validation. But leading PLM vendors like Dassault have invested in industry language models. Dassault acquired generative AI ontology specialist Proxem for its ability to distinguish semantic variations in certification between automotive, aerospace, and life sciences industries.
- Reusability. Leading PLM vendors such as Aras apply AI to vast amounts of data from multiple sources to identify patterns and relationships in an effort to suggest configurable design, bill of materials, and supplier reuse. Aras’ client Fraunhofer developed natural language search, generating a machine-executable query to help untrained users find relevant product data.
- Computer vision. For example, PTC’s Vuforia uses augmented reality to analyze parts on diagrams or in the field to check quality, find misclassifications, or identify substitutes.
- Manufacturing workforce augmentation. AI can parse natural language and turn it into complete problem reports. I’ve not yet seen it, but future generative AI solutions could also enable the factory workforce to use intuitive natural language to describe the task of a robotic system and generate optimized, reliable PLC code.
- Virtual assistance change control. AI already guides PLM users through complex processes such as engineering change management. Chatbots help them prioritize tasks or create new data following best-practice patterns. But generative AI can help organize tasks, approvals, and customer agreements on the critical path to a new product launch. It can document change impact and generate corrective tasks and deliverables.
- Asset and product servicing. For example, PTC’s Servigistics applies AI to internet-of-things data to position service inventory for maximum effect. The ServiceMax copilot will use AI to automate service tasks.
Forrester Research Associate Christian Prandi helped me collate material for this blog. We’ll be collecting further examples and look forward to you sharing with us any that you find, too.