2024 Midyear Review: Still Losing In China, Global Brands Remain Positive
Earlier this year, I published a report exploring the decline of global brands in China’s consumer market, and the concurrent rise of domestic ones. In my latest report, Midyear Review 2024: Global Brands’ Performance In China, our analysis from global brands’ earnings reports reveals that competing in China’s consumer market remains an uphill battle. Five brands in three industries, including Apple, Starbucks, and Tesla, reported negative growth in China due to slower economic growth and intense local competition (see Figure 1).
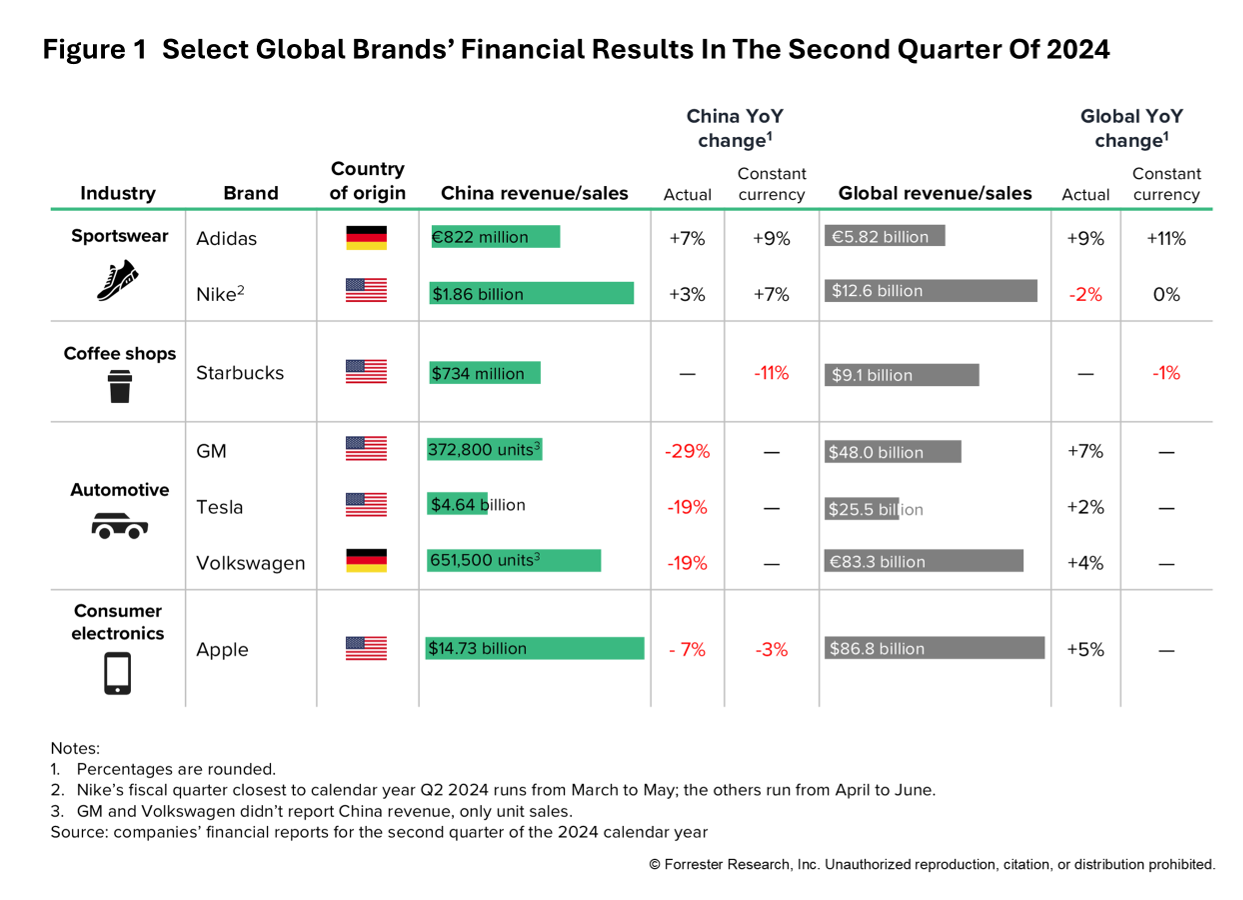
Despite these challenges, most global brands are optimistic about long-term growth in China: Starbucks believes there’s “abundant white space ahead”, and Nike remains “confident in its competitive position in China in the long term”. Apple shares similar sentiments, citing its confidence in its long-term opportunity in China.
Global Brands Can Learn From Peers’ Positive Measures
Despite shrinking performance for most brands we analyzed, there were still some effective strategies, including:
- Localizing strategy. We found that global brands with deep localization strategies performed best in the last quarter. For example, Adidas deepens connections with local consumers through tailored products and experiences in a local-for-local approach. Tesla and Volkswagen outperformed other global automotive brands with their localization efforts – Telsa has a wholly foreign-owned car plant in China, and Volkswagen adopts an “in China, for China” approach.
- Retaining core brand value. Starbucks struggles with economic value against cheaper competitors like Luckin Coffee. Despite avoiding a price war, it uses limited discounts to maintain its premium positioning, focusing on experiential value. Initiatives like a tiered rewards scheme and partnerships with Marriott Bonvoy and Hilton Honors boosted Starbucks Rewards members from 1.6 million to 22 million.
- Leveraging local partners’ cost advantages. Global brands in the electric vehicle sector face intense price competition due to heavy price pressures and consumers’ price sensitivity. It’s crucial for global brands to remain cost-competitive with local firms; they can seek to do so by deepening local partnerships to improve cost efficiency.
Surviving Fierce Local Competition Requires More Than Brand Salience Or Winning Price Wars
Many global brands are losing in China because local competitors are more effective at capturing market share. While almost every global brand we tracked cited intense price pressure from local competitors, only a few, like Volkswagen, recognized local players’ high level of innovation. Domestic brands excel in the Chinese consumer market because of their localized offerings, level and speed of innovation, as well as aggressive marketing. Global brands wishing to succeed in China must keep pace with an offensive localized strategy and have greater ambitions for product innovation and bold marketing.
Forrester clients can access the full report or schedule an inquiry or guidance session for a deeper dive into examples and insights on how global brands can succeed in China.
